二叉树
涉及到二叉树的构造,无论普通二叉树还是二叉搜索树一定前序,都是先构造中节点。
求普通二叉树的属性,一般是后序,一般要通过递归函数的返回值做计算。
求二叉搜索树的属性,一定是中序了,要不白瞎了有序性了
1、二叉树层序遍历
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
// 102.二叉树的层序遍历
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
//checkFun01(root,0);
checkFun02(root);
return resList;
}
//BFS--递归方式
public void checkFun01(TreeNode node, Integer deep) {
if (node == null) return;
deep++;
if (resList.size() < deep) {
//当层级增加时,list的Item也增加,利用list的索引值进行层级界定
List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<Integer>();
resList.add(item);
}
resList.get(deep - 1).add(node.val);
checkFun01(node.left, deep);
checkFun01(node.right, deep);
}
//BFS--迭代方式--借助队列
public void checkFun02(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
que.offer(node);
while (!que.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int len = que.size();
while (len > 0) {
TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll();
itemList.add(tmpNode.val);
if (tmpNode.left != null) que.offer(tmpNode.left);
if (tmpNode.right != null) que.offer(tmpNode.right);
len--;
}
resList.add(itemList);
}
}
}
2、前中后序 遍历
递归版
// 前序遍历·递归·LC144_二叉树的前序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>();
preorder(root, result);
return result;
}
public void preorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
result.add(root.val);
preorder(root.left, result);
preorder(root.right, result);
}
}
// 中序遍历·递归·LC94_二叉树的中序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, list);
list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句
inorder(root.right, list);
}
}
// 后序遍历·递归·LC145_二叉树的后序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
postorder(root, res);
return res;
}
void postorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
postorder(root.left, list);
postorder(root.right, list);
list.add(root.val); // 注意这一句
}
}3、对称二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return true;
return compare(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean compare(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){
if(left==null&&right==null) return true;
if((left==null&&right!=null)||(left!=null&&right==null)||
(left.val!=right.val))
return false;
else{
return compare(left.left,right.right)&compare(left.right,right.left);
}
}
}类似题目 :相同的树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/same-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
return compare(p,q);
}
public boolean compare(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p==null&&q==null)
return true;
if((p==null&&q!=null)||(p!=null&&q==null)||
(p.val!=q.val))
return false;
return compare(p.left,q.left)&compare(p.right,q.right);
}
}另一棵树的子树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
if(s == null && t == null) return true;
if(s == null || t == null) return false;
return compare(s,t)||isSubtree(s.left,t)||isSubtree(s.right,t);
}
public boolean compare(TreeNode p,TreeNode q){
if(p==null&&q==null)
return true;
if((p==null&&q!=null)||(p!=null&&q==null)||
(p.val!=q.val))
return false;
return compare(p.left,q.left)&&compare(p.right,q.right);
}
}4 、二叉树的最大深度
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/description/
深度:距离根节点的距离 前序
高度:距离叶子结点的距离 后序
求深度 用后序遍历最简单 结点的高度 其实就是二叉树的深度。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
return maxdepth(root);
}
public int maxdepth(TreeNode node){
if(node==null)
return 0;
return Math.max(maxdepth(node.left),maxdepth(node.right))+1;
}
}n叉树的最大深度
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> children;
public Node() {}
public Node(int _val) {
val = _val;
}
public Node(int _val, List<Node> _children) {
val = _val;
children = _children;
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(Node root) {
return getMax(root);
}
public int getMax(Node root){
if(root==null)
return 0;
int max=0;
for(Node node:root.children){
int chdepth=getMax(node);
max=Math.max(chdepth,max);
}
return max+1;
}
}5 、二叉树的最小深度
和最大深度的不同是:注意区别左右孩子为空的情况。
最小深度 是指 根节点 到最近叶子结点的距离,叶子结点是指左右孩子都为空的结点
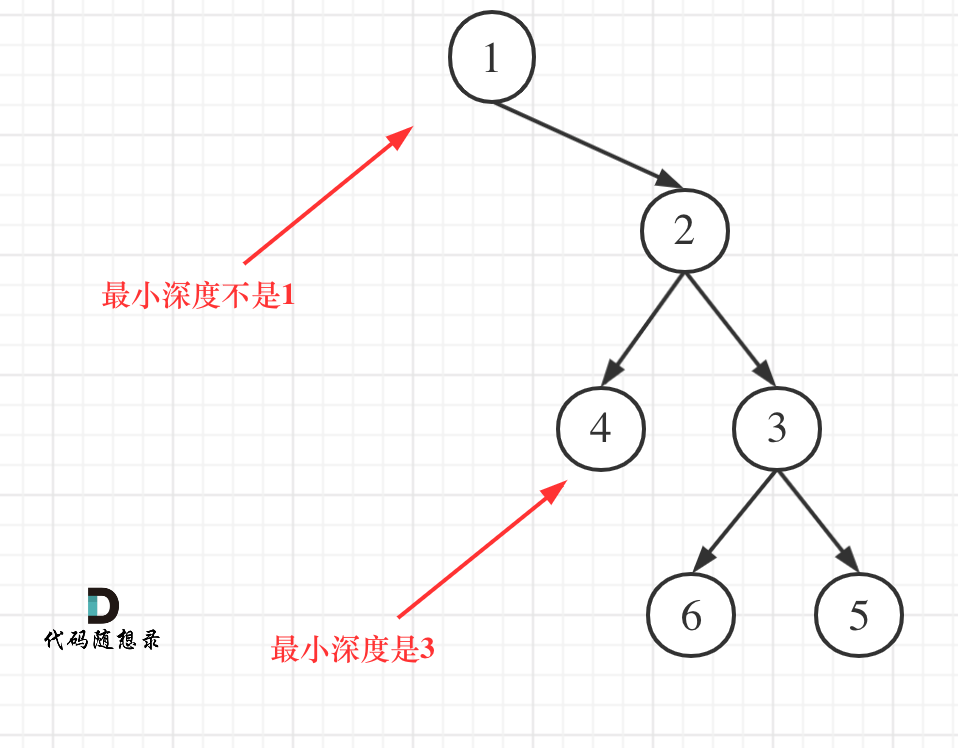
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
if(root.left==null)
{return minDepth(root.right)+1;}
if(root.right==null)
{return minDepth(root.left)+1;}
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left),minDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}6、平衡二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return isBalance(root);
}
public boolean isBalance(TreeNode node){
if(node==null)
return true;
return isBalance(node.left)&&isBalance(node.right)&&(Math.abs(getDepth
(node.left)-getDepth(node.right))<=1);
}
public int getDepth(TreeNode node){
if(node==null)
return 0;
return Math.max(getDepth(node.left),getDepth(node.right))+1;
}
}7 、路径之和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root==null)
return false;
int sum=0;
return hasPath(root,targetSum,sum);
}
public boolean hasPath(TreeNode root,int targetSum,int sum){
if(root==null)
return false;
sum+=root.val;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return sum==targetSum;
}
return hasPath(root.left,targetSum,sum)||hasPath(root.right,targetSum,sum);
}
}注意这里不用回溯!!!递归时 从栈中返回之后 sum的值是当时的值 而不是相加之后的值,
8、从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
return buildTrees(inorder,0,inorder.length,postorder,0,postorder.length);
}
private TreeNode buildTrees(int[] inorder, int inorderbegin, int inorderend, int[] postorder, int postorderbegin, int postorderend){
if(postorderbegin==postorderend)
return null;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[postorderend-1]);
if(postorderend-postorderbegin==1)
return root;
int deliindex=0;
for(int i=inorderbegin;i<inorderend;i++){
if(inorder[i]==root.val){
deliindex=i;
break;
}
}
int leftInorderStart = inorderbegin;
int leftInorderEnd = deliindex;
int rightInorderStart = deliindex + 1;
int rightInorderEnd = inorderend;
int leftPostorderStart = postorderbegin;
int leftPostorderEnd = postorderbegin + (deliindex - inorderbegin);
int rightPostorderStart = leftPostorderEnd;
int rightPostorderEnd = postorderend - 1;
root.left = buildTrees(inorder, leftInorderStart, leftInorderEnd, postorder, leftPostorderStart, leftPostorderEnd);
root.right = buildTrees(inorder, rightInorderStart, rightInorderEnd, postorder, rightPostorderStart, rightPostorderEnd);
return root;
}
}class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
return buildTrees(inorder, 0, inorder.length, postorder, 0, postorder.length);
}
private TreeNode buildTrees(int[] inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd,
int[] postorder, int postorderBegin, int postorderEnd) {
if (postorderBegin >= postorderEnd || inorderBegin >= inorderEnd) {
return null;
}
// The root value is the last element of postorder
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(postorder[postorderEnd - 1]);
// Find the index of the root in inorder array
int deliIndex = 0;
for (int i = inorderBegin; i < inorderEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == root.val) {
deliIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// Calculate the size of the left subtree
int leftSize = deliIndex - inorderBegin;
// Recursively construct the left and right subtrees
root.left = buildTrees(inorder, inorderBegin, deliIndex,
postorder, postorderBegin, postorderBegin + leftSize);
root.right = buildTrees(inorder, deliIndex + 1, inorderEnd,
postorder, postorderBegin + leftSize, postorderEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}
从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildTrees(preorder, 0, preorder.length, inorder, 0, inorder.length);
}
private TreeNode buildTrees(int[] preorder, int preorderBegin, int preorderEnd,
int[] inorder, int inorderBegin, int inorderEnd) {
// Base case: no elements to construct the tree
if (preorderBegin >= preorderEnd || inorderBegin >= inorderEnd) {
return null;
}
// The first element of preorder is the root
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorderBegin]);
// Find the index of the root in inorder array
int deliIndex = 0;
for (int i = inorderBegin; i < inorderEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == root.val) {
deliIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// Calculate the size of the left subtree
int leftSize = deliIndex - inorderBegin;
// Recursively construct the left and right subtrees
root.left = buildTrees(preorder, preorderBegin + 1, preorderBegin + 1 + leftSize,
inorder, inorderBegin, deliIndex);
root.right = buildTrees(preorder, preorderBegin + 1 + leftSize, preorderEnd,
inorder, deliIndex + 1, inorderEnd);
return root;
}
}
9 、最大二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-binary-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return constructMaximumBinary(nums,0,nums.length);
}
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinary(int[] nums,int leftindex,int rightindex){
if(rightindex-leftindex<1){
return null;
}
if(rightindex-leftindex==1){
return new TreeNode(nums[leftindex]);
}
int maxindex=leftindex;
int max=nums[leftindex];
for(int i=leftindex+1;i<rightindex;i++){
if(nums[i]>max){
max=nums[i];
maxindex=i;
}
}
TreeNode node=new TreeNode(max);
node.left=constructMaximumBinary(nums,leftindex,maxindex);
node.right=constructMaximumBinary(nums,maxindex+1,rightindex);
return node;
}
}本题 我没有考虑左闭右开,以及最大值的判断要在当前区间里判断,不要再整个判断。左闭右开的话 那么如果r-l==1 那么证明只有一个结点了,可以直接返回,如果<1,那么就证明左子树或者右子树是空的。
10、合并二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-binary-trees/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root2==null && root1 ==null)
return null;
if(root1!=null && root2 ==null)
return root1;
if(root2!=null && root1 ==null)
return root2;
int nodeval=root1.val+root2.val;
TreeNode node=new TreeNode(nodeval);
node.left=mergeTrees(root1.left,root2.left);
node.right=mergeTrees(root1.right,root2.right);
return node;
}
}自己做出来的 耶
11 、验证二叉搜索树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/description/
中序遍历就能反映出是否是二叉搜索树,要注意的是以下这种错误:
不能单纯的比较左节点小于中间节点,右节点大于中间节点就完事了。
以下代码是错误的
我们要比较的是 左子树所有节点小于中间节点,右子树所有节点大于中间节点。所以以上代码的判断逻辑是错误的。
例如: [10,5,15,null,null,6,20] 这个case:
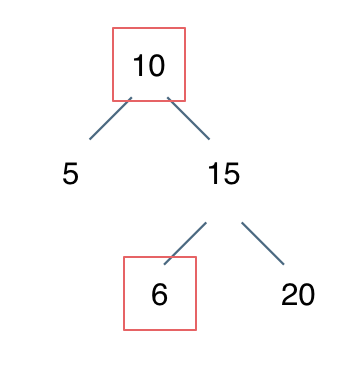
节点10大于左节点5,小于右节点15,但右子树里出现了一个6 这就不符合了!
if (root->val > root->left->val && root->val < root->right->val) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
TreeNode max;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root ==null)
return true;
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
if(max!=null&&root.val<=max.val)
return false;
max=root;
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);
return left&&right;
}
}12 、二叉搜索树中的搜索
https://leetcode.cn/problems/search-in-a-binary-search-tree/description/
要利用二叉搜索树的性质
在二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree, BST)的定义中,左子树的所有节点必须严格小于中间节点的值,而右子树的所有节点必须严格大于中间节点的值。因此,在 BST 中:
左子树:所有节点的值都必须小于当前节点的值。
右子树:所有节点的值都必须大于当前节点的值。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode searchBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
return search(root,val);
}
public TreeNode search(TreeNode root,int val){
if(root==null||root.val==val)
return root;
// 如果目标值小于当前节点值,应该去左子树查找
if (val < root.val) {
return search(root.left, val);
}
// 如果目标值大于当前节点值,应该去右子树查找
return search(root.right, val);
}
}13、二叉搜索树的最小绝对差
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-absolute-difference-in-bst/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
TreeNode pre;// 记录上一个遍历的结点
int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public int getMinimumDifference(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)return 0;
traversal(root);
return result;
}
public void traversal(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return;
if(root.left!=null)
//左
traversal(root.left);
//中
if(pre!=null)
result=Math.min(result,root.val-pre.val);
pre=root;
//右
if(root.right!=null)
traversal(root.right);
return;
}}14、二叉搜索树中的众数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-mode-in-binary-search-tree/description/
依然是双指针
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/class Solution {
TreeNode pre = null;
ArrayList<Integer> resulrt = new ArrayList<>();
int count = 0;
int maxCount = 0;
public int[] findMode(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return new int[0]; // 空树时返回空数组
findMode1(root);
// 将 ArrayList 转换为 int[] 数组
int[] resultArray = new int[resulrt.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < resulrt.size(); i++) {
resultArray[i] = resulrt.get(i);
}
return resultArray;
}
public void findMode1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return;
findMode1(root.left);
if (pre != null && pre.val == root.val)
count++;
else
count = 1;
if (count > maxCount) {
maxCount = count;
resulrt.clear();
resulrt.add(root.val);
} else if (count == maxCount) {
resulrt.add(root.val);
}
pre = root; // 更新 pre
findMode1(root.right);
}
}
15、二叉树的最近公共祖先
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/description/
后序遍历,可以完成从下网上,回溯,要记得把left或right或者root返回。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null)
return null;
if(root==q||root==p) return root;
TreeNode left=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode right=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(left!=null&&right!=null)
return root;
if(left==null&&right!=null)
return right;
if(left!=null&&right==null)
return left;
return null;
}
}16、二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null)
return null;
while(true){
if(root.val>q.val&&root.val>p.val)
root=root.left;
else if(root.val<q.val&&root.val<p.val)
root=root.right;
else
break;
}
return root;
}
}17、二叉搜索树中的插入操作
耶 一次AC
https://leetcode.cn/problems/insert-into-a-binary-search-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
if(root==null)
{
TreeNode node=new TreeNode(val);
return node;
}
if(root.val>val){
TreeNode left= insertIntoBST(root.left,val);
root.left=left;
}
else if(root.val<=val){
TreeNode right= insertIntoBST(root.right,val);
root.right=right;
}
return root;
}
}18、删除二叉搜索树的节点
有以下五种情况:
第一种情况:没找到删除的节点,遍历到空节点直接返回了
找到删除的节点
第二种情况:左右孩子都为空(叶子节点),直接删除节点, 返回NULL为根节点
第三种情况:删除节点的左孩子为空,右孩子不为空,删除节点,右孩子补位,返回右孩子为根节点
第四种情况:删除节点的右孩子为空,左孩子不为空,删除节点,左孩子补位,返回左孩子为根节点
第五种情况:左右孩子节点都不为空,则将删除节点的左子树头结点(左孩子)放到删除节点的右子树的最左面节点的左孩子上,返回删除节点右孩子为新的根节点。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
TreeNode pre=null;
public TreeNode deleteNode(TreeNode root, int key) {
if(root==null)
return null;
if(root.val==key)
{
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return null;
}
else if(root.left!=null&&root.right==null){
return root.left;
}
else if(root.right!=null&&root.left==null){
return root.right;
}
else{
TreeNode cur=root.right;
while(cur.left!=null)
cur=cur.left;
cur.left=root.left;
return root.right;
}}
if(root.val>key){
root.left=deleteNode(root.left,key);
}
else{
root.right=deleteNode(root.right,key);
}
return root;
}
}19、修建二叉搜索树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/trim-a-binary-search-tree/description/
注意:这里如果root的值小于最小值,我们虽然不用去遍历其左子树,因为其左子树的值一定小于low,但是我们不能确定其右子树是否满足条件,所以仍然需要去遍历右子树,如果root的值大于high时同理,我们不用去遍历其右子树,但是我们仍然需要去遍历左子树,
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if(root==null)
return null;
if(root.val<low){
//右子树不一定不满足 需要遍历
//right 代表的是 修剪完之后右子树的根节点
TreeNode right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
return right;
}
else if(root.val>high){
//左子树不一定不满足 需要遍历
//left 代表的是 修剪完之后左子树的根节点
TreeNode left=trimBST(root.left,low,high);
return left;
}
//接收修建完之后的左子树
root.left=trimBST(root.left,low,high);
//接收修建完之后的右子树
root.right=trimBST(root.right,low,high);
//返回根结点
return root;
}
}20 、将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
一次 AC!
就是先找到中间作为根节点,然后左,右,递归即可。
注意区间,这里我使用的是左闭右开。
https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==0)
return null;
return sortedArrayToBST1(nums,0,nums.length);
}
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST1(int[] nums,int low,int high){
if(low>=high){
return null;
}
// int mid=(high+low)/2; //这里为了防止加法溢出 最好使用
int mid=low+(high-low)/2;
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left=sortedArrayToBST1(nums,low,mid);
root.right=sortedArrayToBST1(nums,mid+1,high);
return root;
}
}21、把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/description/
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int sum=0;
public TreeNode convertBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return root;
convertBST1(root);
return root;
}
public void convertBST1(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)
return ;
if(root.right!=null){
convertBST1(root.right);
}
sum+=root.val;
root.val=sum;
if(root.left!=null){
convertBST1(root.left);
}
}
}二叉树篇章 终于写完了


