1、分发饼干
https://leetcode.cn/problems/assign-cookies/description/
class Solution {
public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
if(s.length==0)
return 0;
//从小到大排序
int res=0;
Arrays.sort(g);
Arrays.sort(s);
if(s[0]>=g[g.length-1])
return s.length;
else{
for(int i=0,j=0;i<g.length&&j<s.length;j++){
if(g[i]<=s[j]){
res++;
i++;
}
}
}
return res;}}2、摆动序列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/wiggle-subsequence/description/
class Solution {
public int wiggleMaxLength(int[] nums) {
int prediff=0;
int res=1;
int curdiff=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length-1;i++){
curdiff=nums[i+1]-nums[i];
if((prediff>=0&&curdiff<0)||(prediff<=0&&curdiff>0)){
res++;
prediff=curdiff;
}
}
return res;
}
}默认最右边的是摆动序列加入结果集,默认上一个差为0。
只有摆动时才把 prediff=curdiff,不然如果是一直单调是有平坡就会出错。
3、最大字数和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/description/
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int sum=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int count=0;
int len=nums.length;
if(len==1){
return nums[0];
}
for (int i = 0; i <len;i++) {
count+=nums[i];
sum=Math.max(sum,count);
if(count<0){
count=0;
}
}
return sum;}
}我一直在考虑的是:如果当前值加的是一个负数,那么就重新加,但是这样不对,应该换一种思路:即 如果前面的连续和是一个负数的话,那么应该重新使用下一个数开始加,因为不论下一个数是什么,前面是负数,都会减少后续连续和。
还有一个问题:如果都是负数的话,怎么做?应该让 sum初始化为一个 最小值,这样就能在全部是负数中找到一个值。
4、买卖股票的最佳时机 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii/description/
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int res=0;
for(int i=0;i<prices.length-1;i++){
int diff=prices[i+1]-prices[i];
if(diff>0){
res+=diff;
}
}
return res;
}
}直接ac
5、跳跃游戏
https://leetcode.cn/problems/jump-game/description/
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==1)
return true;
int cover=0;
for(int i=0;i<=cover;i++){
cover=Math.max(i+nums[i],cover);
if(cover>=nums.length-1)
return true;
}
return false;
}
}我刚开始的思路就是错误的,因为我一直在考虑如何到达终点,到底走几步,但是这样子就很复杂,应该换一个角度,即思考覆盖范围,只要覆盖范围能够大于等于最后的数,那么就一定能到达。
6、跳跃游戏Ⅱ
https://leetcode.cn/problems/jump-game-ii/description/
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==1)
return 0;
if(nums.length==1)
return 1;
int res=0;
int curcover=0;
int maxcover=0;
for (int i = 0; i <nums.length ; i++) {
maxcover=Math.max(i+nums[i],maxcover);
if(maxcover>=nums.length-1){
res++;
break;
}
if(i==curcover){
res++;
curcover=maxcover;
}
}
return res;
}
}每走一步,取能够覆盖的最大范围。
7、K 次取反后最大化的数组和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximize-sum-of-array-after-k-negations/description/
class Solution {
public int largestSumAfterKNegations(int[] nums, int k) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int sum=0;
//负数的情况下 消耗尽可能多的k
for (int i = 0; i <nums.length&&k>0 ; i++) {
if(nums[i]<0){
nums[i]=-nums[i];
k--;
}
else
break;
}
//没有负数了,但是k还没消耗完
if(k%2==1){
Arrays.sort(nums);
//奇数 则最小的正变负
nums[0]=-nums[0];
}
//偶数 则不用考虑
for (int i = 0; i <nums.length ; i++) {
sum+=nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
}先用负数消耗k,如果没有消耗完,则用数组中最小的数 ,如果剩余k为偶数,则不用管,如果剩余数为奇数,则直接取一次反即可。
8、加油站
https://leetcode.cn/problems/gas-station/description/
class Solution {
public int canCompleteCircuit(int[] gas, int[] cost) {
int curoil=0;
int sumoil=0;
int start=0;
for (int i = 0; i <gas.length ; i++) {
curoil+=gas[i]-cost[i];
sumoil+=gas[i]-cost[i];
if(curoil<0){
curoil=0;
start=i+1;
}
}
if(sumoil<0){
return -1;
}
return start;
}
}如果curoil<0,那么从i+1开始走,
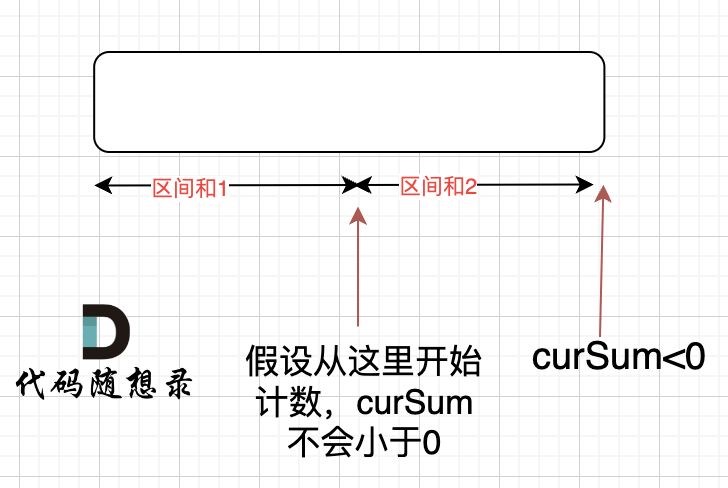
这个时候可能会有疑问?从[0,i]区间就没有一个点也会让curoil<0吗?答案是不会。
如果 curSum<0 说明 区间和1 + 区间和2 < 0, 那么 假设从上图中的位置开始计数curSum不会小于0的话,就是 区间和2>0。
区间和1 + 区间和2 < 0 同时 区间和2>0,只能说明区间和1 < 0, 那么就会从假设的箭头初就开始从新选择其实位置了。
9、分发糖果
https://leetcode.cn/problems/candy/description/
class Solution {
public int candy(int[] ratings) {
int[] candys=new int[ratings.length];//用来保存每个孩子的糖果数
candys[0]=1;
//从前往后 确定右边孩子是否比左边孩子得分高
for (int i = 1; i <ratings.length ; i++) {
if(ratings[i]>ratings[i-1]){
candys[i]=candys[i-1]+1;
}
else
candys[i]=1;
}
for (int i = ratings.length-2; i >=0 ; i--) {
if(ratings[i]>ratings[i+1]){
//左边评分高于右边
candys[i] = Math.max(candys[i], candys[i + 1] + 1);
}
}
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i <candys.length ; i++) {
sum+=candys[i];
}
return sum;
}
}比较两端 分开比较
要注意 判断右边是否大于左边 要从前往后遍历 右边的结果依赖于前边的值。如果从后往前那么右边大于左边没有意义。比较右边小于左边可以。
判断左边是否大于右边,要从后往前遍历,
10、柠檬水找零
https://leetcode.cn/problems/lemonade-change/description/
class Solution {
public boolean lemonadeChange(int[] bills) {
int five = 0;
int ten = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < bills.length; i++) {
if (bills[i] == 5) {
five++;
} else if (bills[i] == 10) {
five--;
ten++;
} else if (bills[i] == 20) {
if (ten > 0) {
ten--;
five--;
} else {
five -= 3;
}
}
if (five < 0 || ten < 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
}虽然我也通过了,但是我的比较复杂,我是使用了map,然后如果不符合,则false,但是可以通过上述方法,直接用变量,最后来判断。
11、根据身高重建队列
https://leetcode.cn/problems/queue-reconstruction-by-height/description/
class Solution {
public int[][] reconstructQueue(int[][] people) {
Arrays.sort(people,(a,b)->{
if(a[0]==b[0]){
return a[1]-b[1];
}
return b[0]-a[0];
});
LinkedList<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
for(int[] p:people){
que.add(p[1],p);
}
return que.toArray(new int[people.length][]);
}
}这里有两个维度,一个身高,一个位置,两个维度时,我们不要同时考虑,而是先考虑一个。
因为是按照身高排序了,所以往前插入的值不会影响前面的位置,因为后边的身高一定比前面的小。
LinkedList.add 方法 第一个参数是下标index,第二个参数是value12、用最少数量的箭引爆气球
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-number-of-arrows-to-burst-balloons/description/
class Solution {
public int findMinArrowShots(int[][] points) {
//左边界从小到大排序
Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]));
int counts=1;
for (int i = 1; i <points.length ; i++) {
if(points[i][0]>points[i-1][1]){
counts++;
}
else{
points[i][1]=Math.min(points[i][1],points[i-1][1]);
}
}
return counts;
}
}左区间从小到大排序,因此之后只用比较上一个点右和该点的左,用这个来比较是否有重叠,并且我们还要判断后续的点是否与其也有重叠,因此,需要更新当前点的右点,为最小的点。
注意,溢出问题
1、使用 a[0] - b[0] 进行比较
Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> { return a[0] - b[0]; });
这种写法在多数情况下是有效的,因为它直接通过减法计算两个整数的差值,从而决定排序顺序。然而,这种方法存在一个潜在的 整数溢出 问题。
整数溢出的风险
定义:当两个整数相减的结果超出了
int类型的表示范围(-2<sup>31</sup> 到 2<sup>31</sup>-1),就会发生溢出,导致结果不准确。
示例:
int a0 = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int b0 = -1; int result = a0 - b0; // 溢出,结果不正确
影响:如果
a[0]和b[0]的差值导致溢出,比较器将返回一个错误的值,破坏了排序的正确性,最终导致程序行为异常(如未通过测试用例)。
2. 使用 Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]) 进行比较
Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]));
这种写法使用了 Integer.compare 方法,它专门设计用于比较两个整数,且 不会出现溢出问题。Integer.compare 返回以下结果:
负数:如果
a[0] < b[0]零:如果
a[0] == b[0]正数:如果
a[0] > b[0]
因此,这种方式是 更安全、更可靠 的实现比较器的方式,尤其在处理可能导致溢出的情况下。
13、 无重叠区间
https://leetcode.cn/problems/non-overlapping-intervals/description/
class Solution {
public int eraseOverlapIntervals(int[][] intervals) {
//左边界从小到大排序
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]));
int counts=0;
for (int i = 1; i <intervals.length ; i++) {
if(intervals[i][0]<intervals[i-1][1]){
counts++;
intervals[i][1]=Math.min(intervals[i][1],intervals[i-1][1]);
intervals[i][0]=Math.min(intervals[i][0],intervals[i-1][0]);
}
}
return counts;
}
}14、划分字母区间
https://leetcode.cn/problems/partition-labels/description/
思路:找每个字母出现的最远下标 如果i==当前最远下标 代表可以分割一次
class Solution {
public List<Integer> partitionLabels(String s) {
List<Integer> list=new LinkedList<>();//存放结果
int[] hash=new int[27];
for (int i = 0; i <s.length() ; i++) {
hash[s.charAt(i)-'a']=i;
}
int left=0;
int right=0;
for (int i = 0; i <s.length() ; i++) {
right=Math.max(right,hash[s.charAt(i)-'a']);
if(i==right){
list.add(right-left+1);
left=right+1;
}
}
return list;
}
}15、合并区间
https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-intervals/description/
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
//左边界从小到大排序
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0], b[0]));
LinkedList<int[]> res=new LinkedList<>();//存放结果
res.add(intervals[0]);
for (int i = 1; i <intervals.length ; i++) {
if(intervals[i][0]<=res.getLast()[1]){
//有重叠 合并
res.getLast()[1]=Math.max(res.getLast()[1],intervals[i][1]);
}
else
//没有重叠
res.add(intervals[i]);
}
return res.toArray(new int[res.size()][]);
}}LinkedList 的 getLast() 函数16、单调递增的数字
https://leetcode.cn/problems/monotone-increasing-digits/description/
从后往前 重点理解 flag作用
class Solution {
public int monotoneIncreasingDigits(int n) {
String s = String.valueOf(n);
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
int flag=s.length();
for (int i = s.length()-1; i >0 ; i--) {
if (chars[i]<chars[i-1]){
chars[i-1]--;
flag=i;
}
}
for (int i = flag; i <s.length() ; i++) {
chars[i]='9';
}
String s1 = String.valueOf(chars);
Integer res = Integer.valueOf(s1);
return res;
}}17、 监控二叉树
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-cameras/description/
理解状态 和四种情况 尤其是最后一种 判断根节点的状态
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
//0 无覆盖 1 有摄像头 2 有覆盖 默认 null 是2状态
class Solution {
int res=0;
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
int rootstate=cover(root);
if(rootstate==0){
res++;
}
return res;
}
public int cover(TreeNode root){
if(root==null) return 2;
//后序遍历
int left=cover(root.left);
int right=cover(root.right);
if(left==2&&right==2){
return 0;
}
if(left==0||right==0){
res++;
return 1;
}//2 和3 的情况不要反
if(left==1||right==1){
return 2;
}
return -1;//其实不会走到这里
}
}

